Allied sectors of Indian Agriculture– Sunrise industry
The critical role that animal husbandry and fisheries play in enhancing farmers’ income, especially with diminishing agricultural holdings, is well-recognized. Schemes such as the Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM), the National Digital Livestock Mission (NDLM), and the National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) incorporate interventions to improve quality, facilitate access to organized markets, and promote the development of indigenous breeds.
Recognizing the increasing relevance of the allied sector in agricultural growth and as a significant source of farm income, several government initiatives are being implemented to enhance productivity, ensure animal health, and facilitate infrastructure development. These interventions focus on improving animal health through the Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme, nurturing entrepreneurship development and per-animal productivity via the National Livestock Mission, and promoting Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) and Self-Help Groups.
The Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) facilitates investments from individual entrepreneurs, private companies, FPOs, and Section 8 companies. The Dairy Cooperative, merged with the Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund in AHIDF, supports key areas such as dairy processing, meat processing, animal feed plants, and breed improvement technology. The government provides a 3 percent interest subvention to borrowers and a credit guarantee of up to 25 percent of the total borrowing.
As of May 2024, 408 projects worth ₹13,861 crore have been sanctioned by lending banks, NABARD, and NDDB, generating 40,000 direct employment opportunities and benefiting more than 42 lakh farmers.
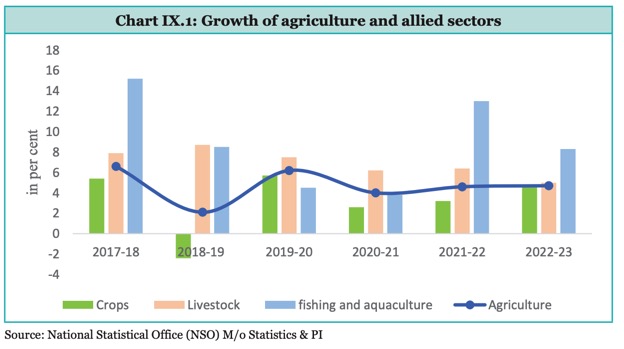
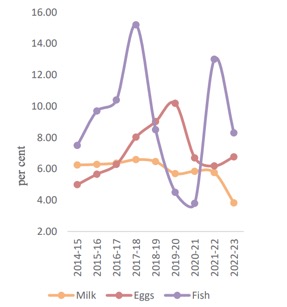
The allied sectors of Indian agriculture are steadily emerging as robust growth centers and promising sources for improving farm incomes. From 2014-15 to 2022-23, the livestock sector grew at an impressive Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.38 percent at constant prices. The contribution of livestock to the total Gross Value Added (GVA) in agriculture and allied sectors increased from 24.32 percent in 2014-15 to 30.38 percent in 2022-23. In 2022-23, the livestock sector contributed 4.66 percent of the total GVA, significantly boosting the per capita availability of milk, eggs, and meat.
Economic Survey 2024, Union Budget
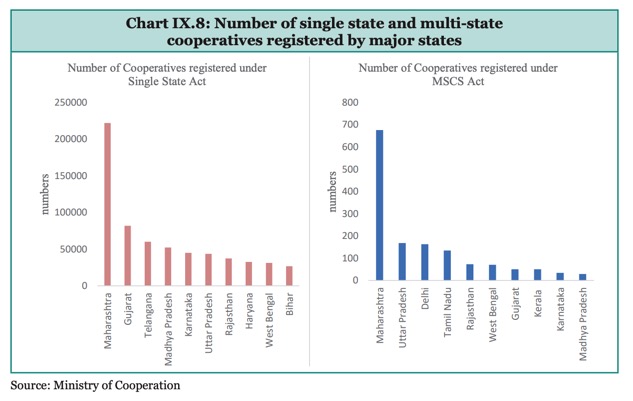
Cooperatives play a crucial role in aggregating produce, enhancing bargaining power, and ensuring better market access for small and marginal farmers, thereby preventing exploitation by middlemen and traders. This is exemplified by the dairy cooperative movement, which focused on small rural producers with 1-2 hectares of land holdings. There is a growing recognition that Primary Agriculture Credit Societies (PACS) can effectively facilitate the convergence of various schemes aimed at farmers’ welfare. By improving the participation of small and marginal farmers in development programs, PACS can enhance the effectiveness and reach of these schemes. In 2023, the government approved a scheme with the goal of establishing PACS in Panchayats and villages that have not yet been covered, targeting completion within the next five years.
The performance of the agriculture sector remains critical for the economy’s growth, achieving an average growth rate of 4.18 percent over the last five years. The growing significance of allied sectors such as animal husbandry, dairying, and fisheries in enhancing farmers’ income underscores the need to tap into the potential of these activities. Smallholder farmers’ incomes cannot be significantly increased by producing rice, wheat, or even millets, pulses, and oilseeds alone. They need to shift to high-value agriculture—fruits and vegetables, fisheries, poultry, dairy, and buffalo meat.